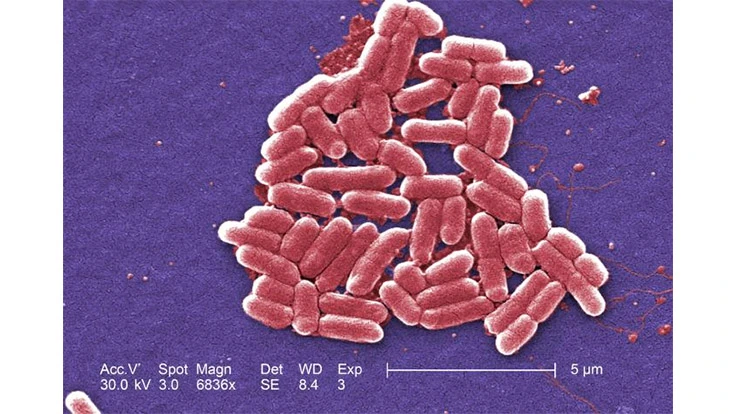
One of the more common culprits of foodborne disease is a pathogenic strain of E. coli. To help prevent illnesses caused by the bacteria in food or water, Pittsburg State University researchers have developed a new nanosensor to rapidly detect its presence. The study appears in the journal ACS Infectious Diseases.
Conventional methods to screen food to find sickness-causing microbes can take as long as 24 hours, which is often too slow to efficiently catch tainted products before they hit store shelves. Faster methods exist, but have limitations. Magnetic resonance, for example, can detect extremely low levels of bacteria, but loses its effectiveness at higher bacteria concentrations. Fluorescence is the opposite. Tuhina Banerjee, Santimukul Santra and colleagues wanted to see if they could combine the two techniques to make a better detector.
The researchers developed a hybrid nanosensor incorporating magnetic resonance and fluorescence. Lab testing of milk showed the detector could sense varying concentrations of the pathogenic strain of E. coli O157:H7 in less than an hour. They also used their sensor to analyze E. coli levels in untreated lake water, which serves as a source of household water in some developing areas. Additionally, the device could be customized to detect a wide range of pathogens beyond E. coli, the researchers say.
Latest from Quality Assurance & Food Safety
- Director General of IICA and Senior USDA Officials Meet to Advance Shared Agenda
- EFSA and FAO Sign Memorandum of Understanding
- Ben Miller Breaks Down Federal Cuts, State Bans and Traceability Delays
- Michigan Officials Warn Recalled ByHeart Infant Formula Remains on Store Shelves
- Puratos USA to Launch First Professional Chocolate Product with Cultured Cocoa
- National Restaurant Association Announces Federal Policy Priorities
- USDA Offloads Washington Buildings in Reorganization Effort
- IDFA Promotes Andrew Jerome to VP of Strategic Communications and Executive Director of Foundation





